Psoriasis is a long-term skin condition that affects how quickly skin cells are produced and replaced. In people with psoriasis, skin cells build up faster than usual, leading to visible changes on the surface of the skin. These changes are often described as patches that may look raised, scaly, or discolored.
This article provides an educational overview of psoriasis, including what it is, how it affects the skin, common ways it is described, and how it may influence daily life. It is for general informational purposes only and does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Understanding How Healthy Skin Normally Works
Healthy skin constantly renews itself. Old skin cells shed naturally as new cells form underneath.
In typical skin renewal:
- New skin cells form deep in the skin
- Cells gradually move toward the surface
- Old cells shed as new ones replace them
This process usually takes several weeks. Psoriasis is associated with changes in this cycle.
What Happens in Psoriasis?
In psoriasis, the skin cell renewal process speeds up significantly. Instead of taking weeks, new skin cells may reach the surface in just days.
Because the body cannot shed cells quickly enough:
- Skin cells accumulate on the surface
- Visible patches may form
- The skin may appear thicker or scaly in affected areas
Psoriasis is commonly described as an immune-related condition involving inflammation.
How Psoriasis Is Commonly Described
Psoriasis can look and feel different from person to person. Educational descriptions often focus on visible skin changes and sensations.
Commonly Reported Skin Changes
- Raised patches of skin
- Scaling or flaking
- Red, pink, or darker discolored areas depending on skin tone
- Clearly defined patch borders
Common Sensations
- Itching
- Dryness
- Tightness
- Sensitivity in affected areas
Not everyone experiences the same appearance or level of discomfort.
Areas Commonly Affected by Psoriasis
Psoriasis can appear on many parts of the body, though certain areas are more commonly discussed.
Frequently affected areas include:
- Scalp
- Elbows
- Knees
- Lower back
- Hands and feet
Some people experience psoriasis in one area, while others notice it in multiple locations.
Common Types of Psoriasis
Educational resources often describe several types of psoriasis based on appearance and location.
Plaque Psoriasis
- Most commonly discussed type
- Features raised, scaly patches
- Often affects elbows, knees, and scalp
Guttate Psoriasis
- Appears as small, drop-shaped spots
- Often noticed on the torso or limbs
Inverse Psoriasis
- Affects skin folds
- Appears smoother and less scaly
- Common in areas like underarms or groin
Pustular and Other Forms
- Less common
- May involve pus-filled bumps or widespread skin changes
These categories help describe patterns but are not used for self-diagnosis.
Factors Commonly Associated With Psoriasis
Psoriasis does not usually have a single cause. It is commonly discussed as involving a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors.
Commonly Mentioned Factors
- Family history of psoriasis
- Immune system activity
- Stress
- Skin injury or irritation
- Certain infections
Triggers and patterns can vary widely between individuals.
Psoriasis and Daily Life
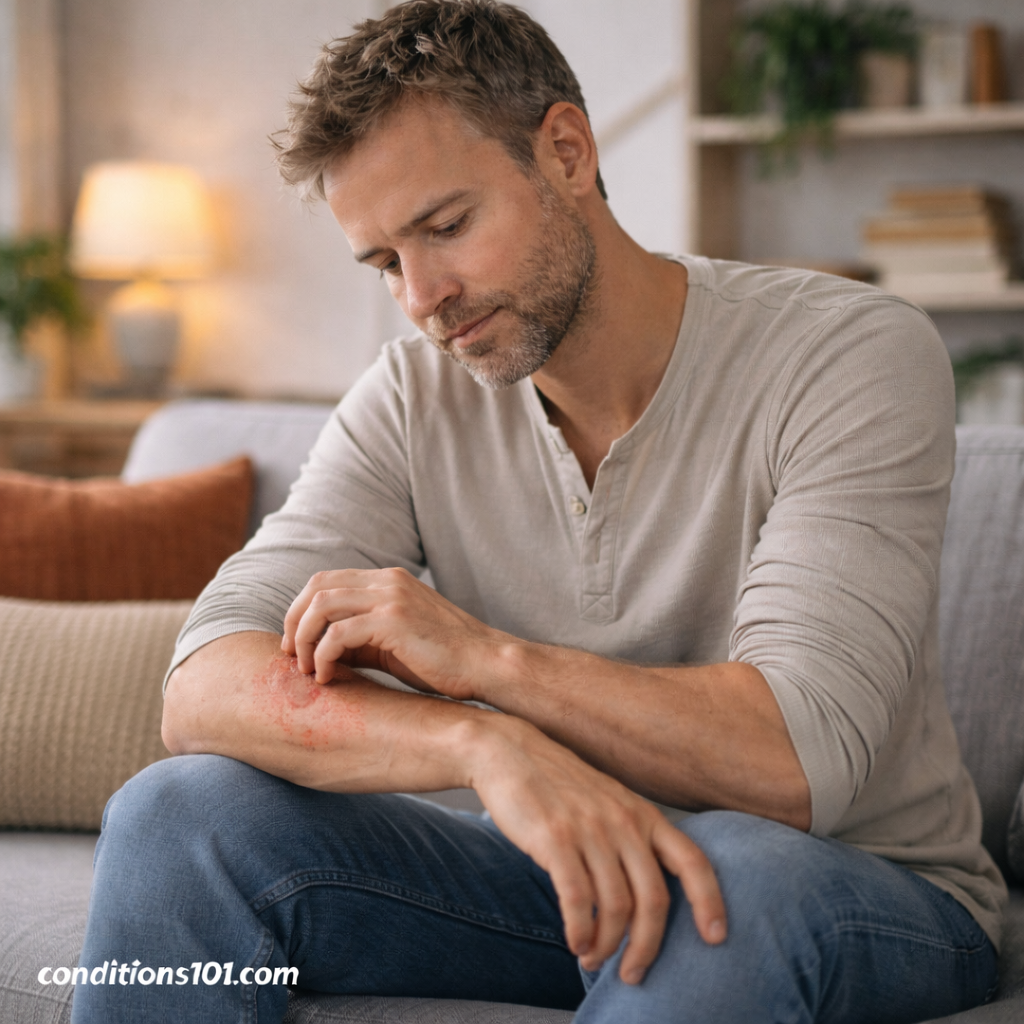

For some people, psoriasis causes mild and manageable skin changes. For others, it may affect comfort, confidence, or daily routines.
Possible Daily Impacts
- Increased time spent on skin care
- Sensitivity to clothing or fabrics
- Awareness of visible skin changes
- Emotional or social discomfort
The day-to-day impact of psoriasis differs from person to person.
Psoriasis Across Different Life Stages
Psoriasis can appear at different ages and may change over time.
Children and Teens
- Psoriasis may be less common but still possible
- Skin changes may affect self-esteem
Adults
- Symptoms may come and go over time
- Stress and lifestyle factors may influence flare patterns
Older Adults
- Skin may be more sensitive
- Symptoms may overlap with other skin changes related to aging
This overview focuses on general patterns rather than individual experiences.
Psoriasis vs. Other Skin Conditions
Psoriasis can sometimes be confused with other skin conditions due to overlapping features.
Psoriasis
- Often well-defined patches
- May involve scaling and thickness
- Tends to be long-lasting or recurring
Other Skin Conditions
- May involve temporary irritation or rashes
- Often respond differently to environmental changes
Professional evaluation is commonly used to distinguish between conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Psoriasis
Is psoriasis contagious?
No. Psoriasis cannot be spread from person to person.
Is psoriasis the same for everyone?
No. Appearance, location, and severity can vary widely.
Is psoriasis a lifelong condition?
Psoriasis is generally described as long-term, though symptoms may fluctuate over time.
Key Takeaways
- Psoriasis is a long-term skin condition involving rapid skin cell buildup
- It commonly causes visible patches and scaling
- Appearance and sensations vary between individuals
- Multiple factors are commonly associated
- Educational understanding supports informed health conversations
